Open source software supply chain lighting plan, waiting for you>>> ![]()
Error log information
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: GC overhead limit exceeded
2020-06-16 10:44:22.004 [http-nio-8083-exec-91] ERROR o.a.c.core.ContainerBase.[Tomcat].[localhost] - Exception Processing ErrorPage[errorCode=0, location=/error]
org.springframework.web.util.NestedServletException: Handler processing failed; nested exception is java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: GC overhead limit exceeded
at org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doDispatch(DispatcherServlet.java:1061)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doService(DispatcherServlet.java:942)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.processRequest(FrameworkServlet.java:1005)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.doGet(FrameworkServlet.java:897)
at javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:634)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.service(FrameworkServlet.java:882)
at javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:741)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:231)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:166)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationDispatcher.invoke(ApplicationDispatcher.java:712)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationDispatcher.processRequest(ApplicationDispatcher.java:461)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationDispatcher.doForward(ApplicationDispatcher.java:384)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationDispatcher.forward(ApplicationDispatcher.java:312)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.custom(StandardHostValve.java:394)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.status(StandardHostValve.java:253)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.invoke(StandardHostValve.java:175)
at org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve.invoke(ErrorReportValve.java:92)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve.invoke(StandardEngineValve.java:74)
at org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.service(CoyoteAdapter.java:343)
at org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Processor.service(Http11Processor.java:367)
at org.apache.coyote.AbstractProcessorLight.process(AbstractProcessorLight.java:65)
at org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$ConnectionHandler.process(AbstractProtocol.java:868)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint$SocketProcessor.doRun(NioEndpoint.java:1639)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SocketProcessorBase.run(SocketProcessorBase.java:49)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread$WrappingRunnable.run(TaskThread.java:61)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
Caused by: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: GC overhead limit exceeded
Cause of the problem
Use the PS command to find out the running PID of the jar, and then check the details of the Java heap. It is found that the memory is 99%
Reason 1: the initial memory configuration is really too small
Reason 2: related code logic problems lead to memory overflow
jmap -heap PID
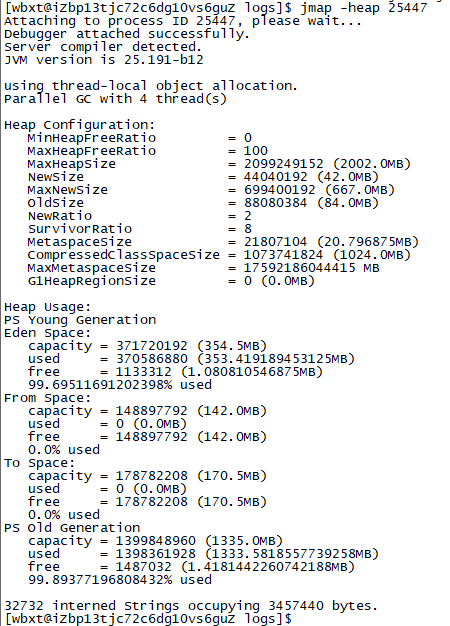
Problem solving
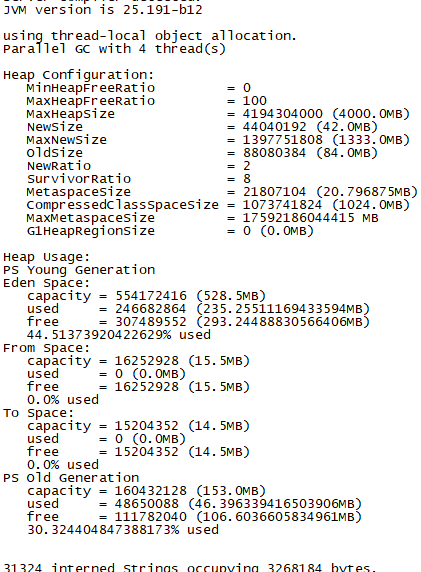
Here is to increase the heap size for the time being
-Xmx4000m -Xms4000m
After adjustment:
Summary
focus on code logic problems. If it’s a code problem, adding heap memory can only delay the generation of java.lang.outofmemoryerror, and eventually lead to memory overflow
JVM parameters
There are three types of JVM startup parameters
Standard parameters (-). All JVM implementations must implement the functions of these parameters and be backward compatible
The non-standard parameter (- x) refers to some configuration parameters at the bottom of the JVM. These parameters can be used by default in general development without any configuration. However, in the production environment, it is not guaranteed that all the JVM implementations are satisfied, so in order to improve the performance, it is often necessary to adjust these parameters in order to achieve the best performance of the system. In addition, these parameters do not guarantee backward compatibility, that is to say, “if there is any change, we will not notify the subsequent version of JDK” (this is the original words on the official website)
Non stable parameter (- XX). This kind of parameter is unstable in the JVM and is not suitable for daily use. In the future, it may be cancelled directly without notice, so it needs to be used carefully
Three main domains of JVM memory
There are three main domains: new domain, old domain and permanent domain
all new objects generated by the JVM are placed in the new domain once an object goes through a certain number of garbage collection cycles, it enters the old domain. The persistent domain is used to store the reflection objects of the JVM itself, such as class and method objects, and GC (garbage collection) will not clean up the persistent domain during the main program runtime (main reason). The new domain and the old domain belong to the heap, and the permanent domain is an independent domain and is not considered a part of the heap
function of main parameters
– XMS: sets the initial size of the JVM memory
– Xmx: sets the maximum memory of the JVM
– XMN: set the size of the new domain (this seems to work only for jdk1.4, but it was abandoned later)
– XSS: set the stack size of each thread (that is, in the same physical memory, reducing this value can generate more threads)
– XX: newratio: set the ratio of the new domain to the old domain. For example, – XX: newratio = 4 means that the ratio of the new domain to the old domain is 1:4
– XX: newsize: sets the initial value of the new domain
– XX: maxnewsize: sets the maximum value of the new domain
– XX: permsize: sets the initial value of the persistent field
– XX: maxpermsize: sets the maximum value of the persistent field
– XX: survivorratio = n: set the ratio of Eden area and two survivorregions in the new domain( Eden area is mainly used to store new objects, while the two survivor areas are used to store objects that survive each garbage collection.)
Similar Posts:
- Web Project Error: javax.servlet.ServletException: Circular view path [registerForm]
- java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: no rxtxSerial in java.library.path
- [Solved] Cannot call sendError() after the response has been committed
- JavaWeb Error:java.lang.NumberFormatException: null
- java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: GC overhead limit exceeded
- java.security.cert.CertificateException: No subject alternative DNS name matching
- [Solved] layui url: rendering data error (thymeleaf)
- [Soloved] Fastdfs Error: java.net.SocketTimeoutException: connect timed out
- HTTP status 500 – servlet. Init () [How to Solve]