When doing this topic today (142. O (1) check power of 2), I encountered an error “bad operate types for binary operator ‘& amp;”
First, paste the code:
public class Solution {
/**
* @param n: An integer
* @return: True or false
*/
public boolean checkPowerOf2(int n) {
// write your code here
if(n<=0)
return false;
return (n&(n-1)==0)?true:false;
}
}Error:
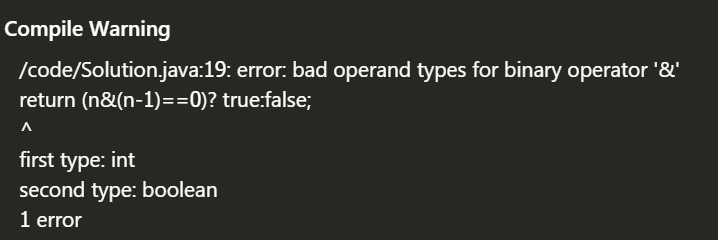
At first, I guessed that it was an operator problem, but I also ruled it out. I always feel that there is something wrong with the “true” and “false” behind, but I can’t find it. Later, I learned that it was really a matter of priority, which might be affected by the assignment (=) operator; The priority of “=” is higher than “=”, which is actually the opposite. The identity operator takes precedence over the bitwise operator, which results in “& amp;” The left is int type, the right is boolean type, sure enough, the basic things still can’t be ignored
So just put “return (n & amp( n-1)==0)? true:false; ” Change to “return ((n & amp( n-1))==0)? true:false; ” That’s it