I want to judge whether there is an element “world” in a collection. If there is, I will add a “JavaEE” element
The practice at that time was as follows:
public class ListIteratorDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a List collection object
List list = new ArrayList();
// Add elements
list.add("hello");
list.add("world");
list.add("java");
// Iterator traversal
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String s = (String) it.next();
if ("world".equals(s)) {
list.add("javaee");
}
}
System.out.println("list:" + list);
}
}But the error exception in thread “main” java.util.concurrent modificationexception was reported
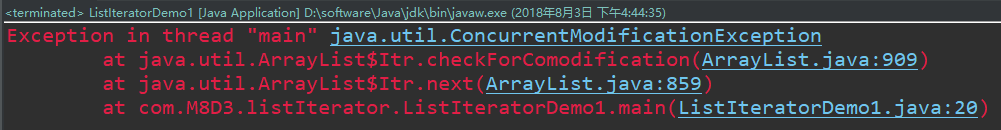
Check the API to know:
Concurrent modificationexception: this exception is thrown when a method detects concurrent modifications to an object, but does not allow such modifications
The reasons are as follows
The iterator depends on the collection. After the judgment is successful, a new element is added to the collection, but the iterator doesn’t know it, so an error is reported. This error is called concurrent modification exception
How to solve it
A: the iterator iterates the element, and the iterator modified element
follows the element iterated just now
b: set traversal element, set modification element (common for)
element added at the end
A’s solution:
public class ListIteratorDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a List collection object
List list = new ArrayList();
// Add elements
list.add("hello");
list.add("world");
list.add("java");
// Way 1: Iterator iterates over elements, iterator modifies elements
// The Iterator iterator, however, has no added functionality, so we use its sub-interface ListIterator
ListIterator lit = list.listIterator();
while (lit.hasNext()) {
String s = (String) lit.next();
if ("world".equals(s)) {
lit.add("javaee");
}
}
System.out.println("list:" + list);
}
}Implementation results:
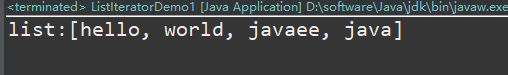
From the result, we can see that the element follows the element of the previous iteration
B’s solution:
public class ListIteratorDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a List collection object
List list = new ArrayList();
// Add elements
list.add("hello");
list.add("world");
list.add("java");
// way 2: set iterate over elements, set modify elements (normal for)
for (int x = 0; x < list.size(); x++) {
String s = (String) list.get(x);
if ("world".equals(s)) {
list.add("javaee");
}
}
System.out.println("list:" + list);
}
}Implementation results:
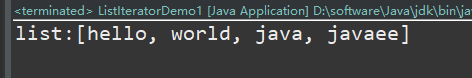
The result shows that the element is added at the end
Similar Posts:
- An error is reported when traversing the list collection to delete elements
- Convert Object to List, avoiding Unchecked cast: ‘java.lang.Object’ to ‘java.util.List
- [Solved] JAVA Beginners’ Error: Exception in thread “main“ java.io.FileNotFoundException
- Eclipse Error:The selection cannot be launched, and there are no recent launches
- [Solved] Java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.Integer cannot be cast to java.lang.Double
- [Solved] Java Call Error: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: wrong number of arguments
- Java container — unsupported operation exception
- Java – Stream has already been operated upon or closed
- [Solved] Hadoop running jar package error: java.lang.exception: java.lang.arrayindexoutofboundsexception: 1