If the asp.net program is running in IIS integrated mode, the_ In start (), just visit context. Request, such as the following code
var request = Context.Request;
An exception is thrown:
Request is not available in this context
You can try if you don’t believe it
This problem will only appear in IIS integrated mode. If it is changed to classic mode, the problem will not appear
Today, I was a little tossed by this problem. In the error log module, we add the operation of recording the current access URL, so that when an error occurs, we can accurately know the access URL that caused the error. We added the following
Code:
HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;
if (context != null && amp; context.Request != null && amp; context.Request.Url != null)
{
return context.Request.Url.AbsoluteUri;
}
Then the updated log module is deployed to the server, but an exception “request is not available in this context” appears in an application, as shown in the following figure:
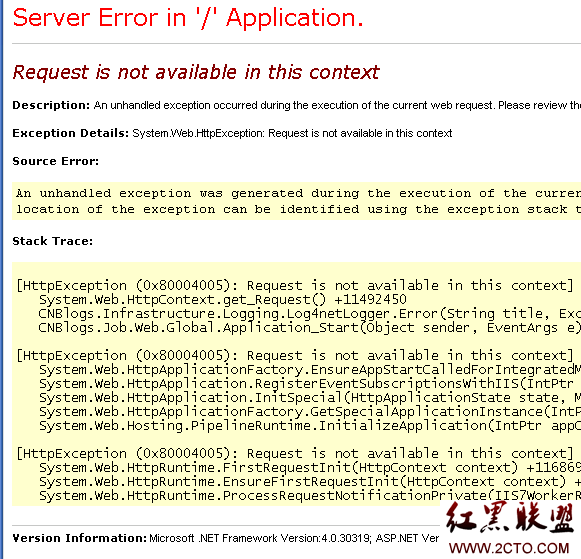
As can be seen from the above exception information, the exception occurred in application_ When accessing the request attribute of httpcontext in start (the application is in the_ Start logs, so it accesses httpcontext. Request)
Using ilspy to view httpcontext
Code:
internal bool HideRequestResponse;
public HttpRequest Request
{
get
{
if (this.HideRequestResponse)
{
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(“Request_ not_ available”));
}
return this._ request;
}
}
As you can see, this exception is thrown when hiderequesresponse = = true, that is, in the application_ In the start phase, the value of hiderequesresponse is true
The puzzle is that since the request property is not allowed to be accessed when hiderequestresponse = = true, why does httpcontext not provide a way for the caller to know that “request is not allowed to be called at this time”. If the caller can check the relevant regulations before calling, he doesn’t have to waste emotion and pay the price (capture the httpexception)
In addition, our requirement is just to get the URL of the current request. If we can’t access the request, we can’t get the URL. Is it in application_ When you start, you can’t get the URL of the current request. This URL is passed from external (IIS) to asp.net runtime, which has nothing to do with the status of asp.net runtime. It’s a bit confusing
Unfortunately, we have to solve the problem first and judge by catching the exception
The code is as follows:
HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;
if (context != null && amp; context.Request != null && amp; context.Request.Url != null)
{
try
{
return context.Request.Url.AbsoluteUri;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
if (ex is HttpException)
{
return string.Empty;
}
}
}
Similar Posts:
- ASP.NET Core – Handle Error on Razor Page
- [Solved] react native TypeError: Network request failed Unable to symbolicate stack trace: The stack is null
- [How to Solve] Unexpected end of file from server
- Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()Class.getClassLoader()
- How to Solve Cannot determine embedded database driver class for database type NONE
- Servlet jump mode sendredirect() and forward ()
- How to Solve Request processing failed; nested exception is java.lang.NullPointerException
- Solve the problem of “resource interpreted as document but transferred with MIME type application / JSON” in IE browser
- Trouble Connecting to sql server Login failed. “The login is from an untrusted domain and cannot be used with Windows authentication”