After MySQL is installed, MySQL directly enters the database
After setting the remote connection, the following error will be prompted:

Prompt: error 1044 (42000): access denied for user ‘@’localhost’ to database ‘MySQL’. The reason is that in the user table of MySQL database, there is an account whose user name is empty, that is, an anonymous account. In fact, it logs in anonymously. It can be seen from the “@ ‘localhost” in the error prompt. Therefore, the solution is shown in method 2
method 1: (applicable to those with incorrect password)
0. Ideas:
By shielding the login password of MySQL, first enter into mysql, and then update the password through the update command
1. Close mysql
Service mysqld stop/Linux
Net stop MySQL// window
2. Shielding permissions
mysqld_ Safe — skip grant table// in Linux
Mysqld — skip grant table// window
Or use the following command
mysqld_ safe –user=mysql –skip-grant-tables –skip-networking & // Using Linux
the screen appears: starting demo from
3. Open a new terminal and input
?MySQL – U root MySQL
MySQL > UPDATE user SET Password=PASSWORD(‘newpassword’) where USER=’root’;
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; // Remember this sentence in the update command, otherwise, if you close the previous terminal, the original error will appear again
MySQL & gt\ q
method 2: (applicable to the presence of empty password)
0. Ideas
Sometimes, although MySQL has an account and a corresponding password. However, due to the existence of a blank password, it will log in to the blank password by default
If you need to delete the account with empty password, you can view all the accounts through the following command
select host,user,password from user;
1. Close MySQL
?Service mysqld stop
2. Shield permissions
?Mysqld_ Safe — skip grant table
the screen appears: starting demo from
3. Start a new terminal to input
# MySQL – U root MySQL
MySQL > delete from user where USER=”; // Delete empty password
MySQL > FLUSH PRIVILEGES;// Remember this sentence, otherwise, if you close the previous terminal, the original error will appear again
MySQL > exit
4. Finally solve the startup error
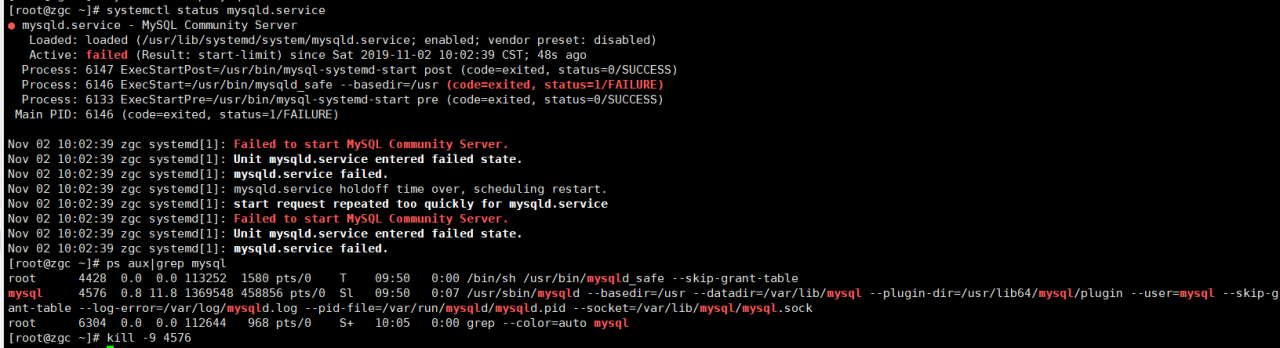
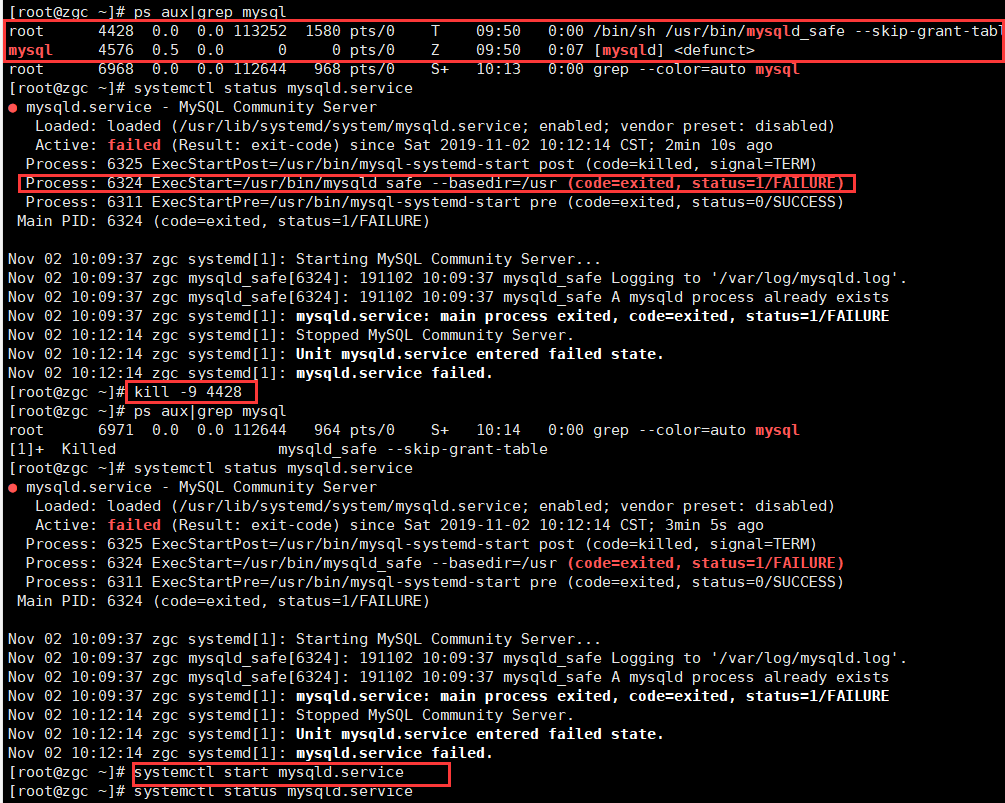
Check the MySQL startup log and find that port 3306 is occupied. Kill the MySQL process and restart the MySQL service
Similar Posts:
- [Solved] MYSQL ERROR 1044 (42000): Access denied for user ”@’localhost’ to database ‘mysql’
- mysql ERROR 1044 (42000): Access denied for user ‘
- MySQLAccess denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ [How to Solve]
- [Solved] MYSQL Install and Login Error: Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@’localhost’ (using password: NO)
- Solve the problem of unknown column ‘password’ in ‘field list’ in MySQL
- [Solved] Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@’localhost’ (using password: NO)
- Linux Login MYSQL Error: ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: YES)
- MYSQL Login Error: mysqladmin: connect to server at ‘localhost’ failed
- Solution to the error of MySQL: unrecognized service (CentOS)
- When installing MySQL database on MAC, the system prompts MySQL: command not found