Any modularization must have import dependency and export interface;
The two main attributes of modularity in ES6 are export and import
Export: interface for exporting modules
Import: the function of importing other modules
1.js
export function test(){
let name = 'cmwang'
return name
}
1.html
<script type="module" >
import { test } from './1.js';
console.log('test', test());
</script>
Both files are directly created locally and run with vscode. Two problems are encountered in this process:
1.When type=”module” is not added to the script, the console output is abnormal:
Uncaught SyntaxError: Cannot use import statement outside a module
2.After adding type=”module”, the console outputs other exceptions:
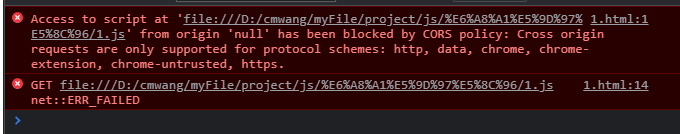
The reason is that the file protocol does not support cross domain in Google browser, and protocols such as HTTP must be used. The reason is because of the browser security policy
Solution:
1) Download and install live server. In the running file, right-click and select open
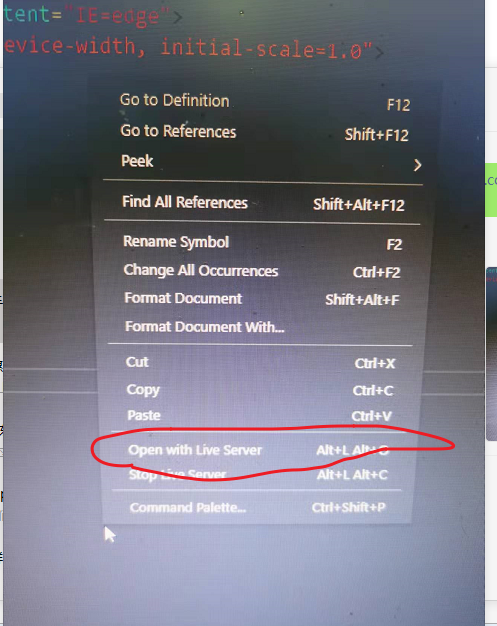
2) Just change your browser
Similar Posts:
- Solution to cross origin read blocking (CORB) blocked cross origin response error
- [Solved] Axios Cross-domain issues: No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin‘ header is present on the requested resource.
- How to Solve .Net 5 webapi cross domain Issue
- JQuery Ajax crossdomain cannot be used in IE [How to Solve]
- export ‘default’ (imported as ‘mod’) was not found in ‘-!../../../../node_module .vue?vue&type=script&lang=ts&’ (possible exports: __esModule)
- Two solutions to cross origin read blocking (CORB) blocked cross origin response error of Web Service API
- A parser-blocking, cross site (i.e. different eTLD+1) script, is invoked via document.write
- Sockjs node/info?T = error reporting solution
- [Two Solutions] Syntax error: unexpected token import